Crozer Emergency Department leaders address sick patient on bus!
September 1, 2022
Women in Emergency Medicine
September 16, 2022HPI: This patient is a 31-year-old male who has a history of hypertension and diabetes who presents to the emergency department with what he describes as a “unremitting throbbing headache” at the left side of the forehead which woke him from sleep around 6am.
ROS: Patient complained of nausea, non-bilious vomiting, photophobia and phonophobia.
Vitals and Physical Exam:
180 kg male, HR 101, BP 148/80, RR 18, SPO2 96% on RA.
Exam notable for left sided forehead tenderness to palpation. His pupils are 8mm, but equal round and reactive to light without visual field defects. His neurological exam does not present any focal neurological deficits.
Imaging studies:
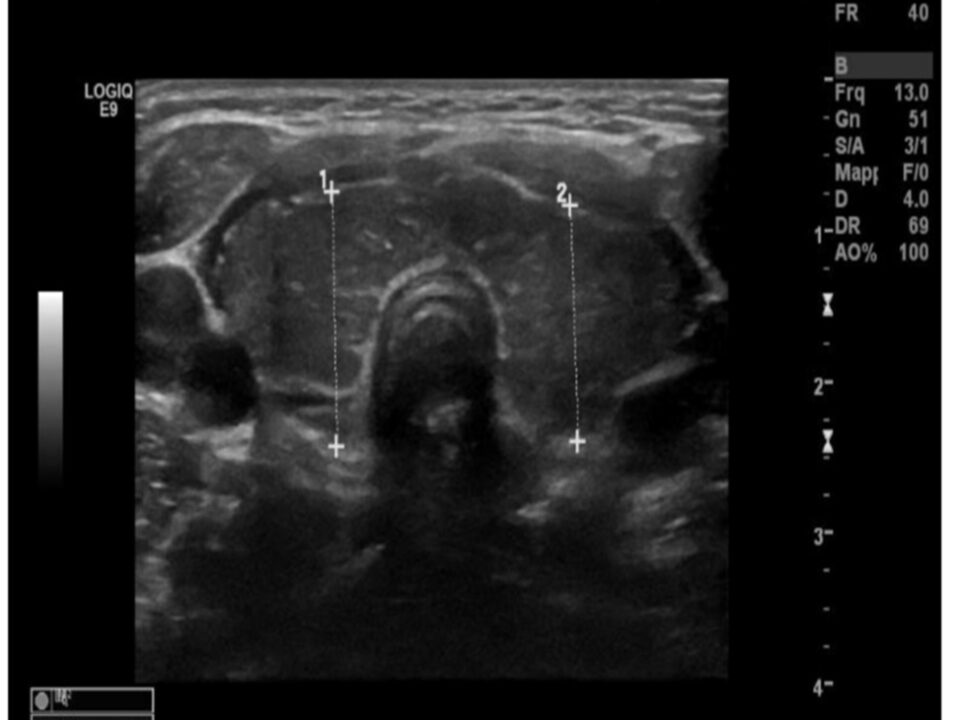
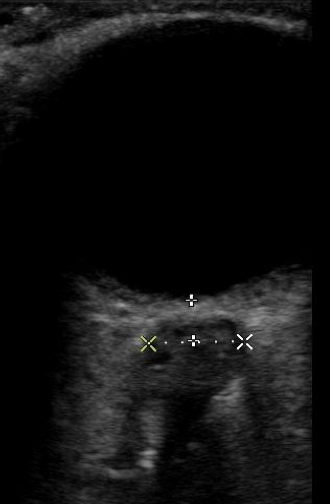
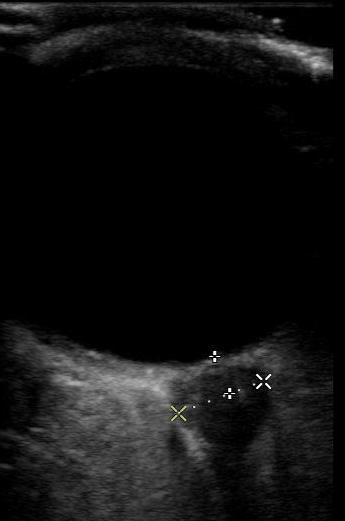
An Ocular Ultrasound was done at bedside in the Emergency Department which showed elevated optic nerve sheath diameter, which was above 5mm bilaterally.
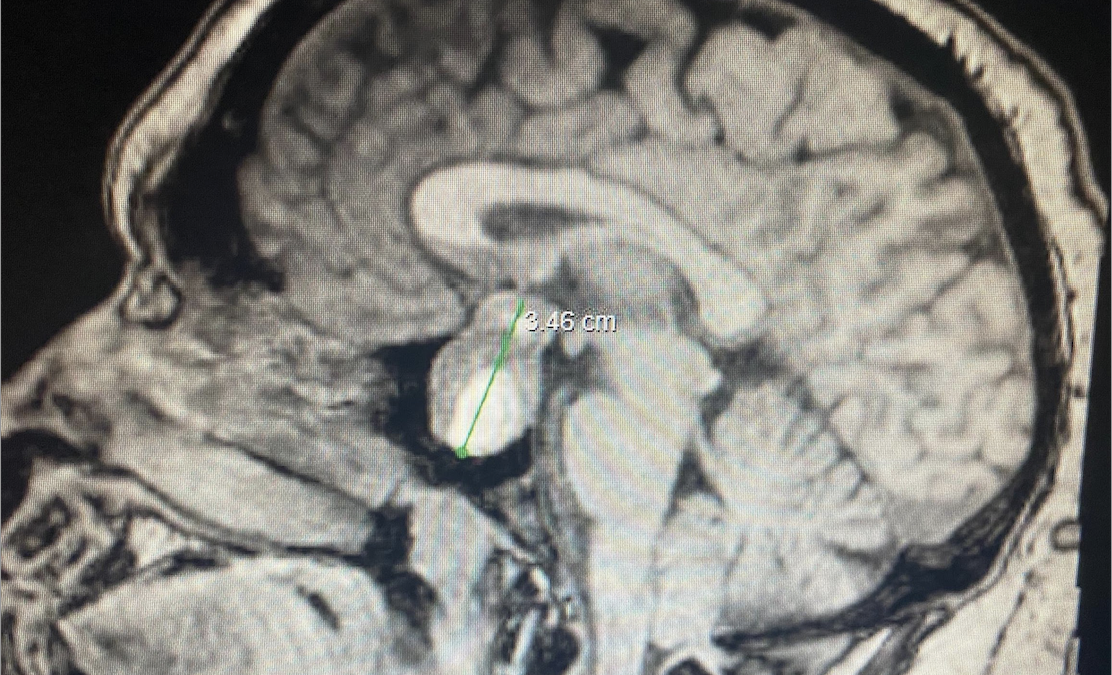
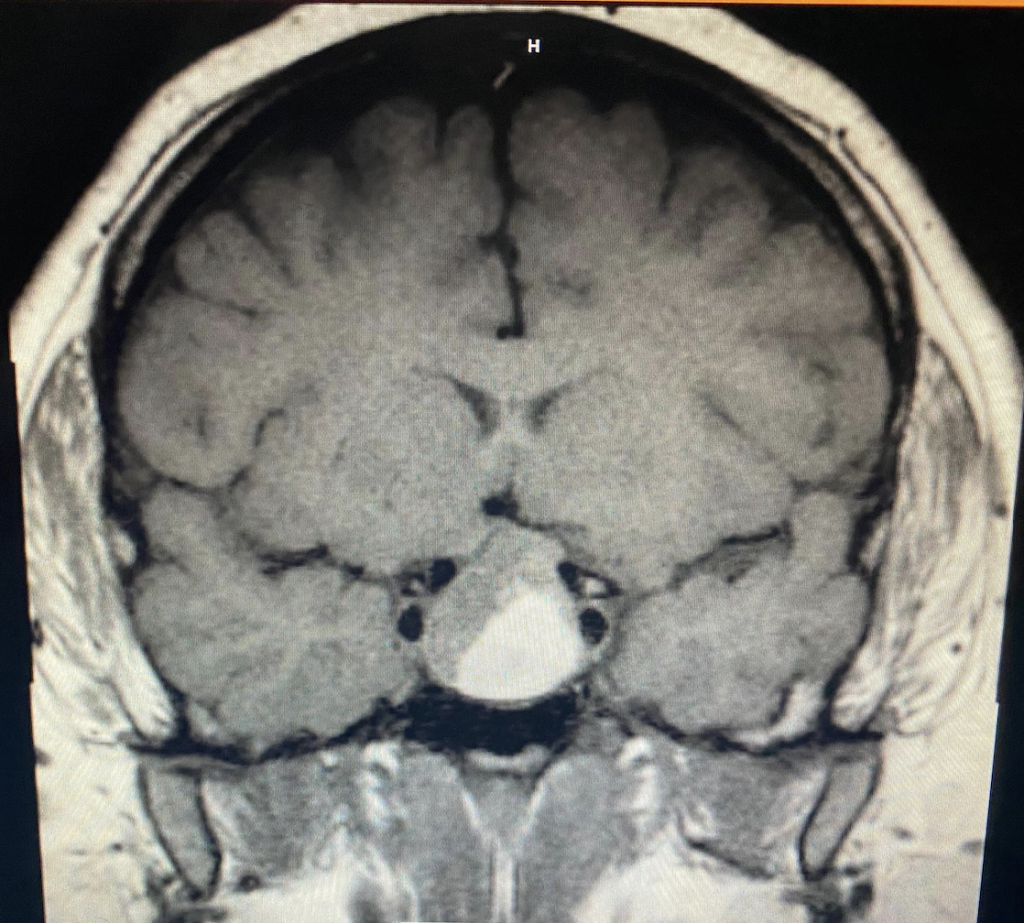
A Non-Contrast Cat Scan was performed in the ED which showed the following:
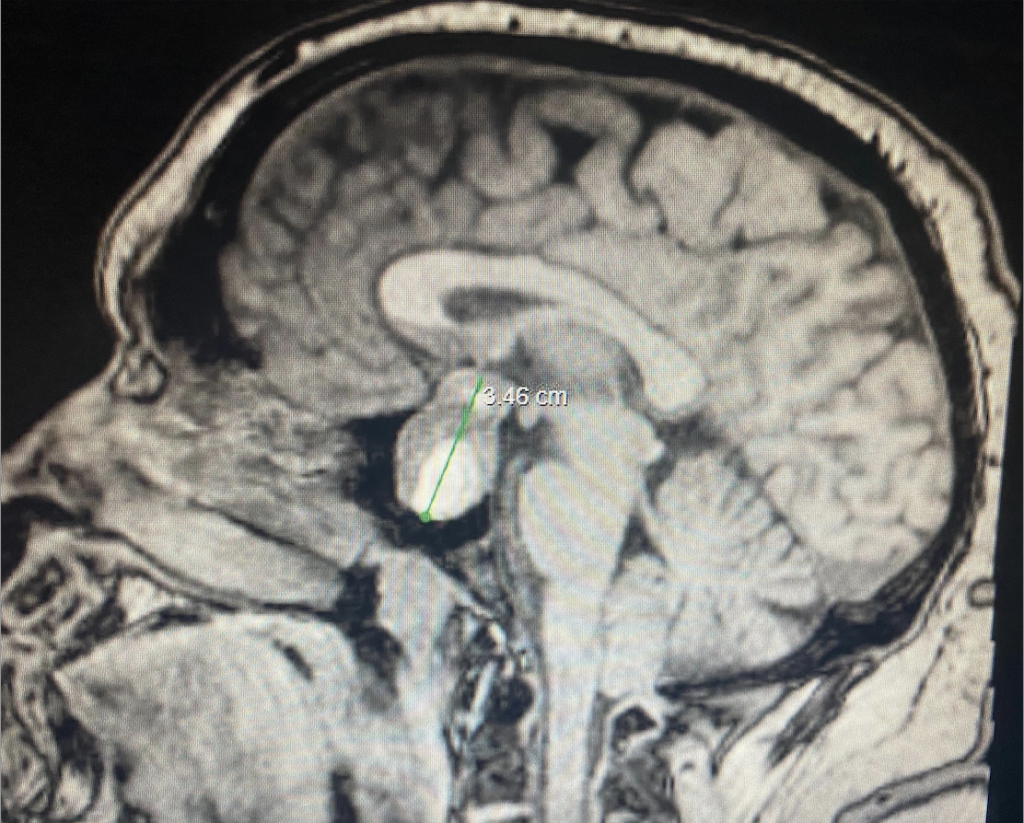
Sagittal view of CT Brain showing 2.5×2.1×2.3cm suprasellar mass.
Hospital Course:
The patient was given symptomatic treatment with Benadryl, Reglan and Decadron, and was admitted to the Neurological ICU for prompt MRI with Gadolinium to further assess the suspected pathology. MRI brain showed sellar mass with suprasellar extension with mass effect on chiasm with mass containing hemorrhagic components. Specifically, the mass was heterogenous with areas of T1 hyperintensity, measuring roughly 2.2 by 2.4 by 3.5 cm (AP x TV x CC). On the surgical pathology report, immunohistochemical staining was positive for Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH), equivocal for Luteinizing hormone and negative for Steroidogenic factor, Growth Hormone, Prolactin and Follicle stimulating hormone. The patient was diagnosed with a Pituitary Macroadenoma, specifically an ACTH tumor, which was managed with a Transsphenoidal resection.
Summary/Take Home Points:
Pituitary adenomas are tumors of the anterior pituitary gland. Some adenomas are considered functioning, in which the cell type that composes them causes increase secretion of one or more hormones of the anterior pituitary, while others are nonfunctioning and don’t secrete hormones but through mass affect can compress surrounding areas causing hormone deficiencies. An ACTH tumor such as what this gentleman had may present with weight gain, mood disorders, and easy bruising, as seen in Cushing syndrome.
The optic nerve sheath diameter is measured in transverse view 3mm posterior from the retina, from outer edge to outer edge. As the optic nerve directly communicates with the intracranial space, it can be used as a proxy to estimate intracranial pressure. Less than 5mm is a normal optic nerve sheath width and is associated with an ICP of less than 20 cc H20. Greater than 5mm is considered an elevated optic nerve sheath diameter, and thus, elevated ICP
Most pituitary adenomas are incidentally found on CT imaging. An MRI with gadolinium is the gold standard test and is necessary not only to distinguish a mass from an aneurysm but also to assess for hemorrhage into the mass. Management of pituitary adenomas depends on the size of the tumor and the presenting sequalae. For nonfunctioning tumors, transsphenoidal resection is recommended in patients with macroadenomas as well as in those with visual deficits, loss of endocrine function or in tumors that have had significant growth over time. For functioning adenomas, although specific treatment depends on the secreted hormone, the universal goal is to decrease hormone secretion, decreased tumor size, and reduce associated complications and mortality. Radiotherapy and or surgery are reserved for functioning adenomas that are resistant to medical therapy.
References
- Russ S, Anastasopoulou C, Shafiq I. Pituitary Adenoma. [Updated 2022 Jul 24]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554451/
- Nieman LK. Update in the medical therapy of Cushing’s disease. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2013;20(4):330-334. doi:10.1097/MED.0b013e3283631809
- The multi-ligand somatostatin analogue SOM230 inhibits ACTH secretion by cultured human corticotroph adenomas via somatostatin receptor type 5 AU Hofland LJ, van der Hoek J, Feelders R, van Aken MO, van Koetsveld PM, Waaijers M, Sprij-Mooij D, Bruns C, Weckbecker G, de Herder WW, Beckers A, Lamberts SW SOEur J Endocrinol. 2005 Apr;152(4):645-54.
- Koziarz A, Sne N, Kegel F, Nath S, Badhiwala JH, Nassiri F, Mansouri A, Yang K, Zhou Q, Rice T, Faidi S, Passos E, Healey A, Banfield L, Mensour M, Kirkpatrick AW, Nassar A, Fehlings MG, Hawryluk GWJ, Almenawer SA. Bedside Optic Nerve Ultrasonography for Diagnosing Increased Intracranial Pressure: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2019 Dec 17;171(12):896-905. doi: 10.7326/M19-0812. Epub 2019 Nov 19. PMID: 31739316.